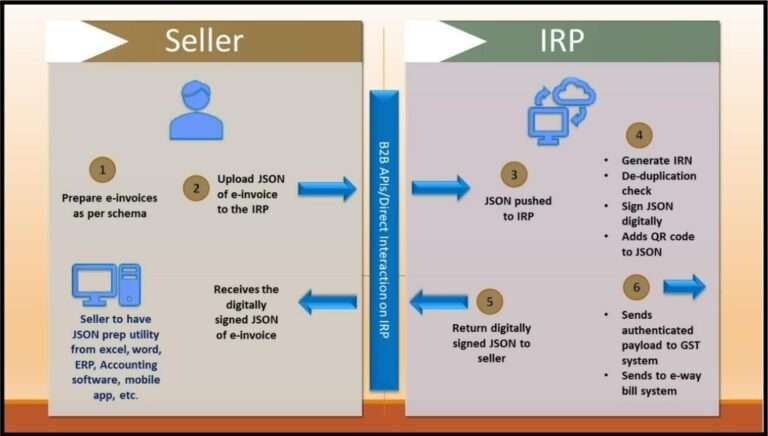
Any reasonable business will not take the chances of bearing above penalties and losing public image. So, even the small companies are rushing to meet the deadlines before 1st April. Businesses have access to a free Excel-based solution from the government to prepare e-invoices. However, this procedure is manual, time-consuming, and potentially error-prone.
Small businesses can also create electronic invoices with the help of an ERP integration mechanism. Here, the e-invoice site is integrated with the taxpayer’s ERP or accounting system to enable automated generation and cancellation of e-invoices in real-time. E-invoice generation is made lightning-fast, smooth, and nearly error-free with the aid of ERP integration. Additionally, some software integrates e-invoicing services with other accounting solutions.
On October 1, 2020, the GST e-Invoicing system went into effect for taxpayers having an aggregate turnover of more than Rs. 500 crores, which includes 3984 firms. The new range of Rs. 100 crores as on January 1st, 2021, has been set up which encompasses 15704 entities. And most recently, on August 1, 2022, it was lowered to Rs. 10 crores, which has resulted in a considerable increase in the number of businesses (i.e., 71570 companies) participating in e-invoicing. This is 18 times the number of businesses involved in the implementation’s early stages.
From the numbers above, we can easily draw the picture which is building the grassroot level of transparency with the help of e-invoicing in the small businesses.
When auto-population is used by these organisations, the GSTR-1 filing procedure is made simpler because several extra steps in the invoicing process are eliminated. Errors and typos are decreased by more automation and less manual input. There is no need to be concerned about your invoice getting misplaced in the mail.
When using e-invoicing software, small businesses can track when an invoice has been delivered, read, and paid. The invoice will have been delivered and received for sure. You may also be able to see when the consumer has viewed the invoice, depending on the service provider. This can make it simple to maintain a track with the aid of a QR code.
The main goal of lowering the e-invoice turnover cap is to detect and prevent tax fraud through compliance improvement. The likelihood of tax evasion is decreased since more taxpayers than in any prior e-invoicing phases fall into the Rs 10 crore and above annual turnover band. Additionally, the larger volume of transactions that these small enterprises experience reveal new compliance challenges.
Eventually, it helps the government as well as the small businesses to run the system smoothly and hassle free. It further increases transparency and reduces human error.